FREE SHIPPING OVER $600 MINIMUM ORDER $400
Botulinum Toxin Therapy For Voice Disorders

Voice disorders can profoundly impact an individual’s communication ability, affecting personal, social, and professional interactions. These disorders may arise from neurological, structural, or functional issues that disrupt the normal functioning of the vocal cords and surrounding muscles. Treatments vary depending on the condition, with one promising option being Botulinum Toxin (commonly known as Botox) therapy.
Botulinum Toxin injections treat various movement disorders, including those affecting the vocal cords. In recent years, this therapy has gained recognition for improving voice quality in patients suffering from certain voice disorders.
Voice Disorders
Voice disorders occur when there are abnormalities in the pitch, loudness, or voice quality that interfere with communication. These disorders can stem from various causes, including neurological conditions, muscle tension, and structural changes in the vocal folds. Some of the most common types of voice disorders treated with Botulinum Toxin include:
- Spasmodic Dysphonia: A neurological condition that causes involuntary spasms in the vocal cords, leading to a strained, choppy, or breathy voice. It has two main types:
- Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia: Characterized by excessive closure of the vocal cords, causing a strained and strangled voice.
- Abductor Spasmodic Dysphonia: Characterized by excessive opening of the vocal cords, leading to a weak, breathy voice.
- Muscle Tension Dysphonia: A condition where excessive tension in the muscles around the larynx disrupts normal voice production, resulting in hoarseness and vocal fatigue.
- Vocal Tremor: A rhythmic, involuntary movement of the laryngeal muscles that affects voice stability and smoothness.
- Neurological Disorders Affecting the Voice: Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, and myasthenia gravis can also contribute to voice disturbances, making speech difficult.
How Botulinum Toxin Works in Voice Therapy
Botulinum Toxin is a neurotoxin derived from Clostridium botulinum, which temporarily blocks nerve signals to the muscles. When injected into overactive vocal muscles, it reduces excessive contractions and spasms, producing a smoother voice.
For individuals with Spasmodic Dysphonia, relaxes the overactive muscles in the larynx, reducing the spasms that cause voice breaks and strain. Botox can decrease the severity of Vocal Tremors, leading to a more stable voice.
Since Botulinum Toxin’s effects are temporary, treatment must be repeated every few months to maintain voice quality. However, many patients find significant relief from their symptoms with regular injections.
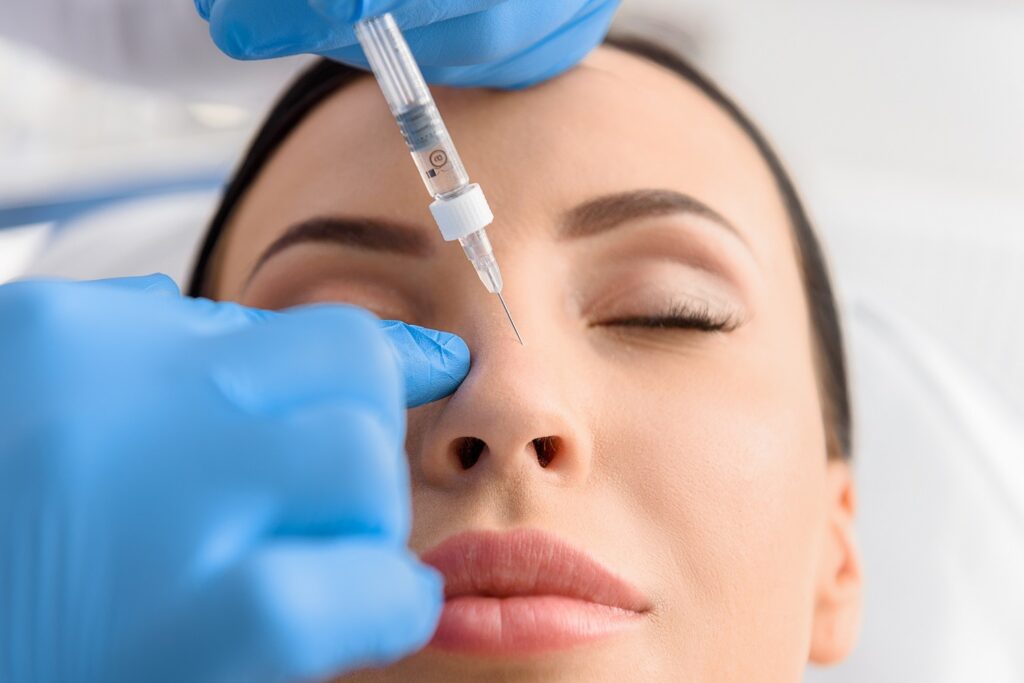
The Procedure of Botulinum Toxin Therapy for Voice Disorders
Before undergoing Botox therapy, patients must be evaluated by an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) or a speech-language pathologist to confirm the diagnosis. This may use:
- A laryngoscopic examination to visualize the vocal cords.
- Acoustic analysis to assess voice quality and function.
- Electromyography (EMG) to evaluate muscle activity in the larynx.
Injection Process:
- Preparation: The patient is seated, and the doctor identifies the target muscles in the larynx.
- Needle Placement: A thin needle is inserted into the vocal cord muscles through the skin.
- EMG Guidance: Some procedures use EMG to ensure precise placement in the affected muscle.
- Injection: A small amount of Botulinum Toxin is injected into the muscle.
- Observation: The patient is monitored for any immediate reactions and voice changes.
The treatment is minimally invasive and often takes only a few minutes. Most patients can resume normal activities the same day, though some may experience temporary voice changes.
Benefits and Effectiveness of Botox Therapy
Botulinum Toxin therapy is one of the most effective treatments for spasmodic dysphonia and related voice disorders. Benefits include:
- Improved Voice Quality: Reduces spasms and voice breaks, leading to a smoother, more natural-sounding voice.
- Non-Surgical Approach: A simple, outpatient procedure with minimal risks.
- Quick Recovery Time: Patients can return to normal activities shortly after treatment.
- Customizable Treatment: The dosage and injection sites can be adjusted based on individual needs.
Many studies have shown that patients experience significant voice improvement after Botox injections, with effects lasting between 3 to 6 months before requiring another session.
Limitations and Side Effects of Botulinum Toxin for Voice Disorders
While effective, Botulinum Toxin therapy is not a permanent solution and comes with some drawbacks:
Limitations
- Temporary Effects: Requires repeat injections every few months.
- Cost Considerations: The therapy can be expensive, and insurance coverage varies.
- Variable Outcomes: Not all patients achieve the same level of improvement.
Side Effects
- Breathiness: Some patients experience a temporarily weak or breathy voice.
- Swallowing Difficulties: Mild difficulty swallowing, especially with liquids.
- Hoarseness: Temporary roughness or changes in vocal tone.
- Rare Allergic Reactions: In very rare cases, allergic responses may occur.
Most side effects resolve within a few weeks as the toxin wears off, and doctors can adjust the dosage to minimize unwanted effects.
Tips for Best Results with Botulinum Toxin Therapy for Voice Disorders
To maximize the effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin therapy and achieve the best possible voice improvement, consider the following tips:
Before the Injection
- Consult a Specialist: Work with an experienced ENT doctor or laryngologist who specializes in Botox for voice disorders.
- Communicate Your Symptoms Clearly: Describe your voice issues in detail so the doctor can target the correct muscles.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports vocal cord health and may aid in recovery after treatment.
After the Injection
- Rest Your Voice: Avoid excessive talking or straining your voice for the first few days post-injection to allow the treatment to take full effect.
- Be Patient with Temporary Changes: Your voice may initially sound weak or breathy, but it typically improves as the Botox settles.
- Adjust Your Speaking Style: If you experience temporary breathiness, practice speaking at a slower pace and using shorter sentences.
Long-Term Management
- Schedule Regular Follow-Ups: Keep track of when your symptoms return and work with your doctor to determine the best timing for repeat injections.
- Consider Voice Therapy: Combining Botox with speech therapy can enhance vocal control and prolong the effects.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Manage stress, avoid smoking, and stay hydrated to keep your voice in optimal condition.
Conclusion
Botulinum Toxin therapy has revolutionized the treatment of voice disorders, particularly spasmodic dysphonia and vocal tremor. By temporarily relaxing overactive vocal muscles, it allows for smoother, more controlled speech, significantly improving the quality of life for those affected.
While the treatment is not permanent and requires regular maintenance, it offers a non-surgical, highly effective approach to managing voice disorders. Patients considering this therapy should consult with a specialist to determine if Botox is the right choice based on their specific condition.
Ultimately, Botulinum Toxin therapy has provided hope for many individuals struggling with voice disorders, helping them regain confidence in their ability to communicate.