FREE SHIPPING OVER $600 MINIMUM ORDER $400
The Importance of Fibroblasts
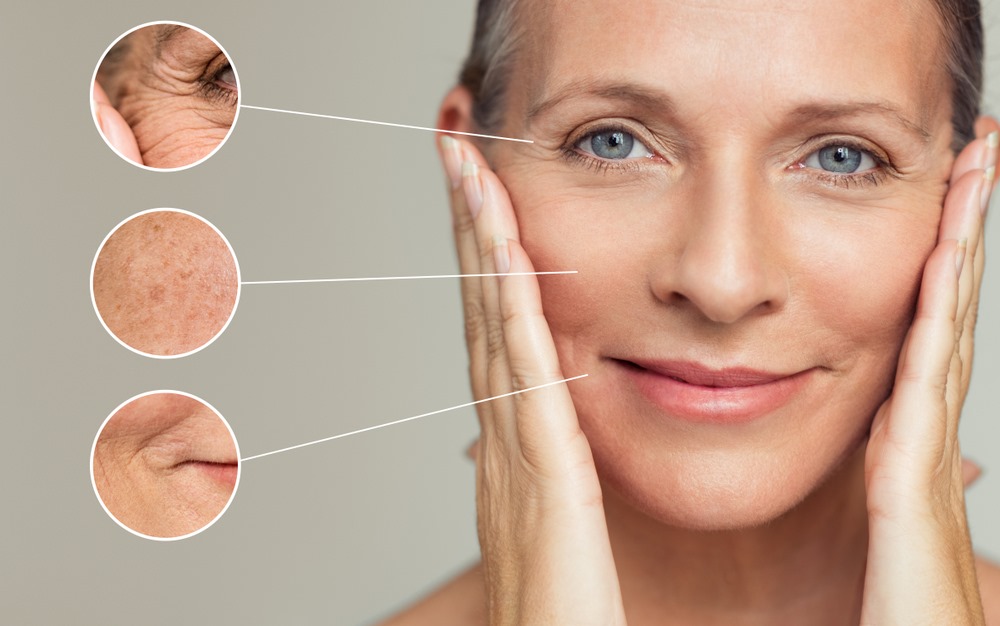
Fibroblasts are fundamental cells in connective tissue that play a critical role in maintaining the structure and integrity of the body. These specialized cells produce the extracellular matrix (ECM) and collagen, which provide strength, elasticity, and support to tissues. Fibroblasts contribute significantly to wound healing, skin regeneration, and organ maintenance, making them essential for overall health.
As we age, fibroblast activity declines, leading to reduced collagen production, wrinkles, and slower wound healing. Research in regenerative medicine, dermatology, and tissue engineering has highlighted the immense potential of fibroblasts in anti-aging treatments, wound care, and disease management.
What Are Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts are specialized cells found in connective tissue throughout the body. Their primary function is to synthesize and maintain the extracellular matrix, which provides structural support to organs, skin, and muscles. Unlike other skin cells such as keratinocytes (which form the outermost layer of the skin), fibroblasts reside in the dermis and deeper layers, constantly working to produce collagen and elastin.
Fibroblasts are highly adaptable, responding to injury and environmental changes by modifying their activity. When the body experiences tissue damage, fibroblasts migrate to the affected site and begin producing new extracellular matrix components, playing a vital role in wound healing. These cells can also transform into specialized types, such as myofibroblasts, which aid in wound contraction and tissue remodeling.
Functions of Fibroblasts
1. Production of Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Fibroblasts are responsible for producing key components of the extracellular matrix, including:
- Collagen: The most abundant structural protein, which strengthens and supports tissues.
- Elastin: A protein that gives tissues their flexibility and resilience.
- Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans: Essential for maintaining hydration and cell communication within tissues.
The extracellular matrix also plays a role in cellular signaling, influencing growth, repair, and immune responses.
2. Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
One of the most critical functions of fibroblasts is their role in wound healing. When an injury occurs, fibroblasts:
- Migrate to the damaged site.
- Proliferate and produce collagen to rebuild tissue.
- Work alongside immune cells and growth factors to accelerate healing.
Fibroblasts prevent chronic wounds and fibrosis (excessive scarring). In conditions such as diabetes, where wound healing is impaired, fibroblast dysfunction can lead to complications like ulcers and infections.
3. Skin Regeneration and Aging
Fibroblasts are crucial for maintaining youthful skin. They help:
- Preserve skin elasticity and firmness.
- Repair daily micro-damage from environmental exposure.
- Regenerate collagen to replace damaged fibers.
However, fibroblast activity slows down, leading to collagen degradation, loss of skin elasticity, and the formation of wrinkles as we age. The factors like UV radiation, pollution, and oxidative stress exacerbated this process.
Fibroblasts in Medical Research and Treatments
1. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Fibroblasts play a major role in regenerative medicine and bioengineered skin grafts for burn victims, chronic wound patients, and reconstructive surgeries. Scientists use fibroblasts to grow artificial skin, helping patients recover from severe injuries.
2. Stem Cell Therapy and Fibroblast-Derived Treatments
Recent research has shown that fibroblasts can be reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which can then be converted into different cell types for regenerative therapies. This breakthrough opens new doors for treating degenerative diseases, such as osteoarthritis and heart disease.
The Role of Fibroblasts in Skincare and Anti-Aging Treatments
Fibroblasts are central to many skincare and dermatological treatments aimed at reducing signs of aging and improving skin health.
Collagen Production and Anti-Aging
A decrease in fibroblast activity leads to collagen loss, which results in fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin. To counteract this:
- Skincare products containing retinoids, peptides, and growth factors help stimulate fibroblast function.
- Microneedling and laser therapy create controlled micro-injuries, triggering fibroblast-mediated collagen production.
Exosome-Based Skincare
Exosomes are tiny vesicles that carry signaling molecules between cells. Research suggests that exosome-based therapies can enhance fibroblast activity, leading to improved skin regeneration and repair.
Factors That Affect Fibroblast Function
Several factors influence fibroblast activity and their ability to maintain healthy tissue:
Aging and Cellular Senescence
- With age, fibroblasts lose their ability to divide and function efficiently.
- Cellular senescence (a state of permanent cell cycle arrest) leads to reduced collagen production and skin thinning.
Environmental Damage and Lifestyle Factors
- UV radiation is the leading cause of fibroblast damage, accelerating skin aging through oxidative stress.
- Pollution and smoking introduce toxins that degrade collagen and impair fibroblast function.
- A poor diet lacking essential vitamins and amino acids can hinder fibroblast regeneration.
Inflammation and Chronic Diseases
- Chronic inflammation from conditions like diabetes and autoimmune disorders can impair fibroblast activity.
- Excessive inflammation leads to fibrosis, where excess collagen creates rigid, non-functional tissue.
How to Support and Maintain Healthy Fibroblast Function
Taking proactive steps can help maintain fibroblast health and prevent premature aging.
Nutritional Support
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) : Essential for collagen synthesis and fibroblast function.
- Amino Acids (Glycine, Proline, Lysine): Building blocks for collagen production.
- Antioxidants (Vitamin E, Polyphenols): Protect fibroblasts from oxidative stress.
Skincare and Lifestyle Choices
- Use sunscreen daily to protect fibroblasts from UV damage.
- Stay hydrated to maintain ECM balance and skin elasticity.
- Exercise regularly to improve blood circulation and fibroblast activity.
Emerging Therapies
- Peptide-based treatments that mimic fibroblast growth factors.
- Exosome and stem cell therapies for enhanced skin regeneration.
Conclusion
Fibroblasts are indispensable for maintaining healthy connective tissue, aiding wound healing, and preserving youthful skin. Their role extends beyond cosmetic concerns, impacting regenerative medicine, cancer research, and tissue engineering.
As fibroblast activity naturally declines with age, taking proactive measures—such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, using fibroblast-activating skincare, and exploring regenerative therapies—can help slow aging and promote tissue repair.
Future research on fibroblast behavior, stem cell applications, and innovative skincare treatments holds great promise for improving health and longevity. By understanding and supporting these vital cells, We can unlock new possibilities for healthier skin, faster healing, and advanced medical treatments.